 Pigs are kept for the production of pork and bacon. Most breeds, if properly managed and fed are capable of producing either pork or bacon. Small-scale pig farmers in the rural areas have largely sustained the Industry. These producers keep on average 2-5 pigs under very poor hygienic and management conditions. There are just a few commercial pig farmers in the country. Unlike the dairy and beef industries, the pig farming industry has largely been unable to attract any foreign and internal investment. This has been exacerbated by the high costs of inputs especially in intensive pig production. The major constraints to pig farming include; diseases and parasites, poor breeding, capital investment, inadequate advisory services, inadequate research, lack of organized marketing, lack of processing plants and poor product quality.
Pigs are kept for the production of pork and bacon. Most breeds, if properly managed and fed are capable of producing either pork or bacon. Small-scale pig farmers in the rural areas have largely sustained the Industry. These producers keep on average 2-5 pigs under very poor hygienic and management conditions. There are just a few commercial pig farmers in the country. Unlike the dairy and beef industries, the pig farming industry has largely been unable to attract any foreign and internal investment. This has been exacerbated by the high costs of inputs especially in intensive pig production. The major constraints to pig farming include; diseases and parasites, poor breeding, capital investment, inadequate advisory services, inadequate research, lack of organized marketing, lack of processing plants and poor product quality.
Why we do pig farming ?
- To produce meat fairly quickly and to get some income from it
- To produce industrial goods such as leather and bristles etc.
- Pigs produce very high value manure which is useful for enriching our soil
What are the advantages of pig farming ?
- Pigs grow very rapidly from 1.5kg at birth to 90kg in 170 days only
- Pigs can be raised on small land especially where land holdings are small
- They produce many young ones. You can raise 20 pigs from one female pig (sow) in a year
- Pig production has low labor requirements.
- Pigs are mainly fed on maize and other grains and root tubers which can normally be bought at very low prices during peak seasons of harvesting.
- Pigs can also be raised on pasture and other crop residues and agro industrial by products.
- Pigs give quick returns on your investment
Common breeds of pigs :
- Large White : It is white in color with erect ears and a ditched face. It produces many piglets and is fairly hardy.
- Landrace : Has drooping ears, white in color with long and big body. It has a long straight snout. It is commonly crossed with the large white.
- Duroc Breed : It is mahogany to red in colour. Has good mothering ability. It is resistant to stress and is adaptable to various environmental conditions. It is very useful in cross breeding programme.
- Crosses : It is common to find crosses of Large white and Landrace. These crosses are very good when used as sows for breeding.
Selection of pigs for breeding:
- Select good gilts from sows of a superior breed that wean 9-10 piglets per litter and that are known to be good mothers.
- Selected gilts should have at least 12-14 teats so that a large litter can be easily nursed.
- Gilts should be healthy with strong legs and well developed body and thigh muscles.
- Beginners in pig farming are advised to start with about 1-2 gilts/sows and progress as more experience and skill is gained.
Management of pig farming :
- Housing in pig farming : Before you venture into pig production decide on the management system you would wish to practice depending on the resources available. Both semi intensive and intensive systems will require pigs to be housed. Good housing is very important in pig production for the following reasons:
- It helps in disease and parasite control.
- It reduces the labor in husbandry and management tasks like feeding and handling.
- It protects the pigs from harsh environmental and climatic conditions.
- Housing keeps out unnecessary intruders.
- The pigs are easily observed when housed.
Materials used for construction of a pig house:
- Local materials: wooden poles, bamboo poles, grass thatch etc. These are cheap but do not last long.
- Manufactured /purchased materials: Blocks/bricks, cement, galvanized iron sheets etc. These are expensive but are the best to use because they are more long lasting. Whatever material you use for the construction of a pig house it is advisable to use concrete for the floor or to compact the floor hard.
Care of the sow and baby pigs : Your pig house should besides the common pens have a farrowing pen (place where the sow delivers). This should be clean, disinfected, dry and warm before farrowing. Leave it for at least 7 days before sow is moved in. Provide fine bedding e.g. shavings, sour grass, sawdust, sand or bagasse etc. It should be maintained dry and soft.
Day of farrowing : Many piglets die at this time. Up to 35% of your piglets born alive may die before weaning. The commonest causes of death at this stage are due to:
- Crushing of piglets by the mother
- Starvation
- Born weak
- Diarrhea
- Chilling (cold) etc.
These losses can be minimized by having somebody present at farrowing. Other causes should be identified and precaution taken.
Management of piglets :
- Once farrowing is completed make sure all piglets are nursing. Any excess piglets for the number of functional teats should be transferred to another sow. If there is no other sow, bottle feed with cow’s milk
- Sweetened with glucose. Transfer at 3-4 days of age without masking odors.
- Clip the needle teeth, cut the navel cord leaving about 2.5 – 3.5cm (1-1.5 inches) of which should be dipped in a 7% iodine solution.
- After 2-3 days treat piglets for anemia with 2-3 ml of injectable iron.
- Provide creep feed at 7 days of age. Change feed daily.
- Treat with iron again after 2 weeks.
- Deworm after 3-5 weeks and then move sow and piglets to nursery. If litters are mixed in a nursery, litters should not be more than one week difference in age and do not mix more than four litters per pen.
- Wean at 56 days (8 weeks).
- Remember to remove the sow from the piglets and not vice versa.
- Deworm piglets regularly
- Spray them for lice and mange mites prior to moving them out of nursery at 7-8 weeks.
- Replace the sow after the 6th litter or after 4-5 years of age. If its production is still good, leave it until its production falls below the average of the herd.
- Seek advice from your extension worker/veterinarian wherever possible.
- Regularly spray disinfectant Viraclean in pig house ,it will help to prevent viral diseases .
Suggested targets to achieve :
- Reproduction rate – 10-11 pigs born alive per litter
- 2 litters/sow/year – 20-22 pigs born alive/sow/year
- Survival rate – 85% of pigs born alive should be reared to weaning (17- 18.7/sow/year
- Growth rate – 90kg live weight in 170 days with a carcass yield of 77% or 500gms/day over a lif time.
- Food conversion efficiency of 3.5kg
- Aim at marketing the pigs for slaughter as porkers at the age of 4-6 months when they will have attained the weight of 45-65kg
- Production life span of at most 5 years for the sows.
Feeds and feeding : Feeds take about 70% of the total cost of production. Therefore use feeds efficiently and economically in order to make profit. Use cheaper, lower grade feed stuff and supplement with more nutritious feeds. Provide feed requirements according to the different categories of pigs and the condition e.g. piglets, weaners, growers, pregnant sows and sows, suckling piglets.
What should you feed your pigs ?
- Carbohydrates/Energy feeds: e.g. maize, corn, sorghum, cassava, sweet potatoes (root & vines), banana peels etc.
- Protein/Body building feeds: e.g. blood meal (up to 5%), cotton seed meal (up to 10%), fish meal (up to 5%), meat and bone meal (up to 5-10%), milk and milk by-products and soya bean meal (up to 10%), sunflower meal (up to 15%).
- Minerals: calcium, phosphorus, iron etc. The best minerals and vitamin supplements for pig is Amino Power.
- Vitamins: These are purchased and added to the feed ration, for this purpose a good multi vitamin products is Growvit Power.
- Water: Water must always be available. Sanitized water is very important and yet it is always forgotten.Always use water sanitizer Aquacure in water.
Health : Always keep your pigs healthy and look out for signs of disease.
Common diseases of pigs :
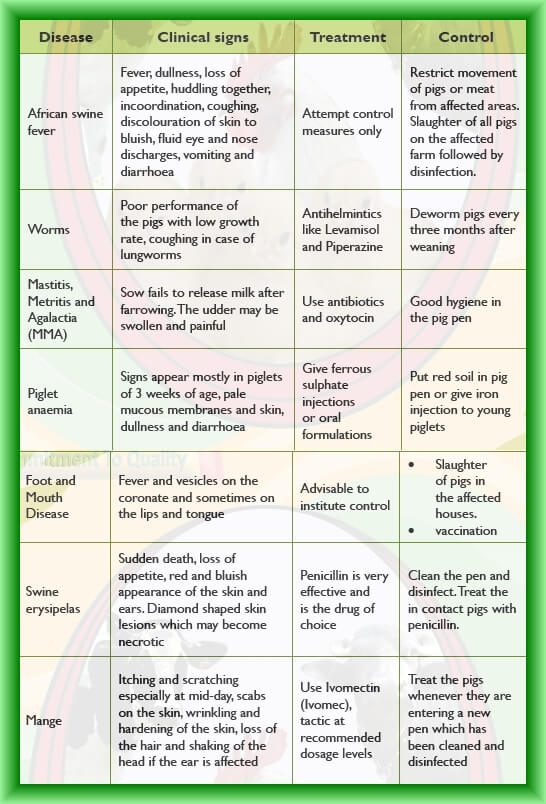
NB: For details on treatment of these diseases and others, consult a veterinarian.
Keeping records: Records are essential for monitoring both technical and economic efficiency. They should cover the following aspects;
- Boar performance
- Sow productivity
- Weaner growth
- Grower / Finisher efficiency
You should also read this book How To Do Profitable Pig Farming
If you are into pig farming or cattle related business & want to earn maximum profit in your business then please join our Facebook group How To Do Profitable Poultry & Cattle Farming ?
It is an Unique Combination of 46 Powerful Amino Acids, Vitamins & Minerals .It is strongest amino acid for poultry & cattle with a remarkable result and quality. Composition: Each 100 ml contains: Histidine: 105 mg Indication & Benefits :
Dosage : For 100 Birds: Broilers : 10-15 ml. Layers : 15-20 ml. Breeders : 15-20 ml. For Cattle: Packaging : 500 m.l. 1 ltr. & 5 ltr. | A Double Power Cattle & Poultry Liver Tonic for preventing hepatic disorders – diseases and better FCR. Composition: Each 10 ml contains: Tricholine Citrate : 1500 mg Protein Hydrolysate : 100 mg Vitamin B 12 : 4 mcg Inositol : 10 mg Methyl Donors : 66 mg Selenium : 7 mcg Vitamin -E : 20 mg Biotin : 6 mcg Base enriched with liver stimulants- q.s. Indication & Benefits :
Dosage : For 100 Birds : Broilers : 8-10 ml. Layers : 10-15 ml. Breeders : 25-30 ml. For Cattle: Cow, Buffalo & Horse : 30-50 ml each animal per day. Calves : 20-30 ml each animal per day. Sheep, Goat & Pig : 10-15 ml each animal per day. Should be given daily for 7 to 10 days, every month or as recommended by veterinarian. Packaging : 500 m.l., 1 ltr. & 5 ltr. |

 Pigs are kept for the production of pork and bacon. Most breeds, if properly managed and fed are capable of producing either pork or bacon. Small-scale pig farmers in the rural areas have largely sustained the Industry. These producers keep on average 2-5 pigs under very poor hygienic and management conditions. There are just a few commercial pig farmers in the country. Unlike the dairy and beef industries, the pig farming industry has largely been unable to attract any foreign and internal investment. This has been exacerbated by the high costs of inputs especially in intensive pig production. The major constraints to pig farming include; diseases and parasites, poor breeding, capital investment, inadequate advisory services, inadequate research, lack of organized marketing, lack of processing plants and poor product quality.
Pigs are kept for the production of pork and bacon. Most breeds, if properly managed and fed are capable of producing either pork or bacon. Small-scale pig farmers in the rural areas have largely sustained the Industry. These producers keep on average 2-5 pigs under very poor hygienic and management conditions. There are just a few commercial pig farmers in the country. Unlike the dairy and beef industries, the pig farming industry has largely been unable to attract any foreign and internal investment. This has been exacerbated by the high costs of inputs especially in intensive pig production. The major constraints to pig farming include; diseases and parasites, poor breeding, capital investment, inadequate advisory services, inadequate research, lack of organized marketing, lack of processing plants and poor product quality.






















































